The Mannich Reaction
Abstract
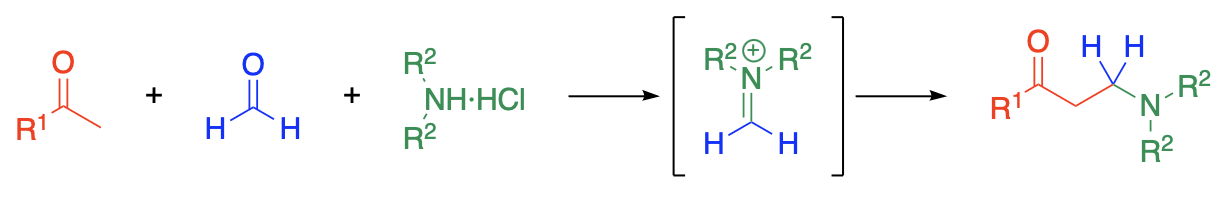
The Mannich reaction consists in the condensation of ammonia or a primary or secondary amine, usually as the hydrochloride, with formaldehyde and a compound containing at least one hydrogen atom of pronounced reactivity. The essential feature of the reaction is the replacement of the active hydrogen atom by an aminomethyl or substituted aminomethyl group. The product from acetophenone, formaldehyde, and a secondary amine salt is an example. The product to be expected from a Mannich reaction involving an ammonium salt is a primary amine. The mechanism of the Mannich reaction has not been established.

