The Acetoacetic Ester Condensation and Certain Related Reactions
Author(s):
Hauser, Charles R.; Hudson, Jr., Boyd E.
Volume:
1
Published:
1942
Abstract
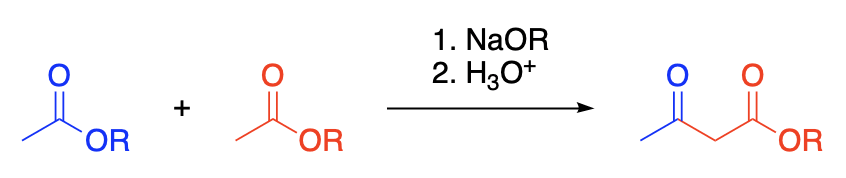
The acetoacetic ester condensation consists in the reaction, in the presence of certain bases, of an ester having hydrogen on the alpha-carbon atom with a second molecule of the same ester or with another ester to form a beta-ketoester. The bases capable of effecting such reactions include sodium alkoxides, triphenylmethylsodium, sodium amide, and certain Grignard reagents. Metallic sodium effects certain condensations, the sodium alkoxide which is formed in the reaction mixture probably serving as the active condensing agent. The classical example of the acetoacetic ester reaction is the formation of acetoacetic ester itself by the condensation of ethyl acetate by means of sodium ethoxide.

